Advanced Encryption Standard(AES) is a symmetric encryption algorithm. AES is the industry standard as of now as it allows 128 bit, 192 bit and 256 bit encryption.Symmetric encryption is very fast as compared to asymmetric encryption and are used in systems such as database system. Following is an online tool to generate AES encrypted password and decrypt AES encrypted password. It provides two mode of encryption and decryption ECB and CBC mode. For more info on AES encryption visit this explanation on AES Encryption.
' A secret key has no structure. It's nothing more than N bytes of data. ' It should typically be random data, or bytes that resemble random data such ' as the hash of a password. ' The number of bytes in the secret key defines the bit-strength of an encryption ' algorithm. For example, AES with a 32-byte key is 256-bit AES. I am using AES-CBC to provide confidentiality for protocol messages. I want to allow the receiver to know the secret key by using a key ID. For this I hash the secret key to generate a key ID. Every time the sender wants to send a message, the sender appends the key ID to the message to allow the receiver to bind the key ID with a secret key. Mar 05, 2015 Using Key/SecureKey. Now, let's show a simple example of creating an encrypted standard string with the use of a key. AES encryption only supports 128-bit (16 bytes), 192-bit (24 bytes) or 256-bit key (32 bytes) lengths, so we'll need to create or generate an appropriate key.
Also, you can find the sample usage screenshot below:
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On Devglan, You Can Consider:
- Like us at: or follow us at
- Share this article on social media or with your teammates.
- We are thankful for your never ending support.
Usage Guide
Any plain-text input or output that you enter or we generate is not stored on this site, this tool is provided via an HTTPS URL to ensure that text cannot be stolen.
For encryption, you can either enter the plain text, password, an image file or a .txt file that you want to encrypt. Now choose the block cipher mode of encryption. ECB(Electronic Code Book) is the simplest encryption mode and does not require IV for encryption. The input plain text will be divided into blocks and each block will be encrypted with the key provided and hence identical plain text blocks are encrypted into identical cipher text blocks. CBC mode is highly recommended and it requires IV to make each message unique. If no IV is entered then default will be used here for CBC mode and that defaults to a zero based byte[16].
The AES algorithm has a 128-bit block size, regardless of whether you key length is 256, 192 or 128 bits. When a symmetric cipher mode requires an IV, the length of the IV must be equal to the block size of the cipher. Hence, you must always use an IV of 128 bits (16 bytes) with AES.
AES provides 128 bit, 192 bit and 256 bit of secret key size for encryption. Things to remember here is if you are selecting 128 bits for encryption, then the secret key must be of 16 bits long and 24 and 32 bits for 192 and 256 bits of key size. Now you can enter the secret key accordingly. By default, the encrypted text will be base64 encoded but you have options to select the output format as HEX too.
Similarly, for image and .txt file the encrypted form will be Base64 encoded.
Below is a screenshot that shows a sample usage of this online AES encryption tool.
AES decryption has also the same process. By default it assumes the entered text be in Base64. The input can be Base64 encoded or Hex encoded image and .txt file too. And the final decrypted output will be Base64 string. If the intended output is a plain-text then, it can be decoded to plain-text in-place.
But if the intended output is an image or .txt file then you can use this tool to convert the base64 encoded output to an image.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.Other Free Tools
“There’s as many atoms in a single molecule of your DNA as there are stars in the typical galaxy. We are, each of us, a little universe.” ― Neil deGrasse Tyson, Cosmos
Contents

- Conclusion
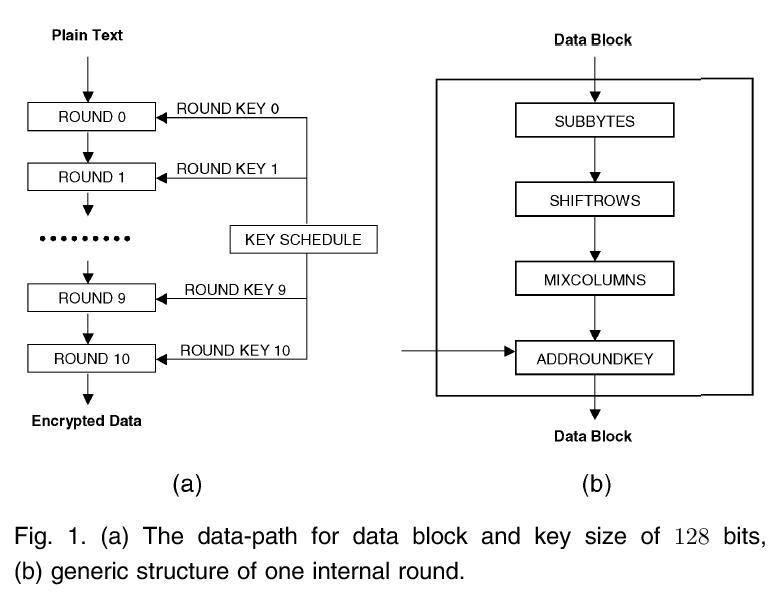
1. Introduction
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a standard for encryption and decryption that has been approved by the U.S. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) in 2001. It is more secure than the previous encryption standard DES(Data Encryption Standard) and 3DES(Triple-DES). You should be using AES for all symmetric encryption needs in preference to DES and 3DES (which are now deprecated).
Symmetric Encryption refers to algorithms that use the same key for encryption as well as decryption. As such, the key should be kept secret and must be exchanged between the encryptor and decryptor using a secure channel.
The core java libraries provide good support for all aspects of encryption and decryption using AES so no external libraries are required. In this article, we show you how to properly perform encryption and decryption using AES with just the core java API.
[Note: Check out how to use AES for file encryption and decryption in python.]
2. The Imports
We need the following import statements for the program.
Generate Aes Secret Key
3. Generate an Initialization Vector (IV)
When using AES with a mode known as CBC (Cipher Block Chaining), you need to generate an initialization vector (IV). In the CBC mode, each plaintext block is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before being encrypted. So you need an initialization vector for the first block. To produce different ciphertext with each run of the encryption (even with the same plaintext and key), we use a random initialization vector.
To generate the IV, we use the SecureRandomclass. The block size required depends on the AES encryption block size. For the default block size of 128 bits, we need an initialization vector of 16 bytes.
From the initialization vector, we create an IvParameterSpecwhich is required when creating the Cipher.
You can save the initialization vector for transmission along with the ciphertext as follows. This file can be transmitted plainly i.e. no encryption is required.
4. Generating or Loading a Secret Key
If you do not already have a key, you should generate one as follows:
If you have a key (maybe one generated previously and stored securely), you can load it from a binary key file using the following code:
If you need to save a generated key for future usage (maybe for loading using the above code), you can do it as follows:
5. Creating the Cipher
The Cipher object is the one that handles the actual encryption and decryption. It needs the secret key and the IvParameterSpec created above.
When encrypting, create the Cipher object as follows:
For decryption, you need to load the initialization vector and create the IvParameterSpec.
Now you can create the Cipher object:
6. Encrypting a String
Once the Cipher object is created, you can perform the encryption. The encryption process works with byte arrays.
To encrypt a String, first convert it to a byte array by encoding it in UTF-8. Then write the data to a file as follows:
7. Decrypting Back to a String
Read back encrypted text and convert it to a String as follows:
8. Encrypting a File
The procedure for encrypting a file is a bit more involved. Read the input data in a loop and invoke Cipher.update(). If a byte array is returned, you can write it to the output file. https://ebooksnew178.weebly.com/blog/conic-art-mac-free-download. Finally wrap up with a Cipher.doFinal().
Invoke the encryption as follows:
9. Decrypting a File
The outfile obtained from the above procedure can be decrypted quite simply by specifying the decrypt mode as follows:
And that covers the whole story of encryption and decryption using AES.
Conclusion
Generate A Secret Key Using Aes Code
The process for encrypting and decrypting using AES is a bit involved. First you generate an IV (initialization vector) and then generate (or load) a secret key. Next you create a cipher object which you can use for encryption and decryption.